Consonants are classified in contrast to vowels sounds produced with the vocal tract completely open. Consonant any speech sound such as that represented by t g f or z that is characterized by an articulation with a closure or narrowing of the vocal tract such that a complete or partial blockage of the flow of air is produced.

Consonants Definition And Examples
Place of articulation.

. What are some of the major characteristics of consonants. The order used is the following. O b m w v ð d n z l dʒ ʒ r.
Consonants are classified into two groups as follows. The term continuants is often reserved for consonant sounds even though vowels are included. This exercise provides practice at describing the consonants of Standard English using the parameters of articulation.
When it comes to consonant characteristics which term is better to have memorized. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds the other being the consonantVowels vary in quality in loudness and also in quantity lengthThey are usually voiced and are closely involved in prosodic variation such as tone intonation and stress. What are the three major dimensions used to describe consonants and what do they refer to.
What are the classification of consonants. In certain positions esp. What can happen to airflow through the vocal tract during consonant production.
Pulmonic consonants are described according to three features. What are the basic universal distinctions between vowels and consonants. A consonant sound where the airflow passes exclusively through the nose instead of the mouth.
A consonant sound where the airflow becomes noisy and turbulent because it only has a very small space to travel through in the mouth. Occlusives such as plosives affricates and nasals contrast with Continuants. Select all that apply - State of the Glottis - Place of Articulation - Manner of.
Glide is the general term for a consonant which corresponds in this way to a vowel. What are the characteristics categories used to describe consonants. Three of the English vowels introduced earlier required a sequence of two IPA symbols.
Consonants are classified in contrast to vowels sounds produced with the vocal tract completely open. Examples include fin and van Dentalinterdental - This creates sound between the teeth like in. This might seem like a violation of the principle that there should be a one-to-one relationship between sounds and.
Approximants occupy a kind of linguistic grey area between vowels and consonants in fact w and y are also known as semivowels. Manner of articulation. In most cases the active articulators are the lips and tongue.
Bilabial - You use both lips to create the sound such as the beginning sounds in pin bust well and the ending sound in seem Labiodental - This uses the lower lip and upper teeth. Consonants are usually classified according to place of articulation the location of the stricture made in the vocal tract such as dental bilabial or velar the. Voiced consonants if the vocal cords vibrate.
Think of sounds like f s and sh Most languages have fricatives but not all. Consonant Place of Manner of Voicing. Consonants can be voiced or -voiced.
Consonants are classified in contrast to vowels sounds produced with the vocal tract completely open. Consonants have two primary classifying. That is their formation depends upon an egressive outward-flowing airstream initiating in the lungs.
Thus in the word skinflint below the consonant descriptions can be shown as. In order to describe the place of articulation the active and passive articulator need to be known. Consonants that are like vowels approximants.
K g and ɳ are all velar sounds. The last four consonant sounds on the above list y w r l are produced with less mouth constriction than other consonants and in linguistics are called approximants. Consonants are sounds produced with the vocal tract restricted or completely closed.
Consonants have two primary classifying. Whether the vocal cords vibra. Place of articulation state of glottis manner of articulation TF.
Aj aw and ɔj. Think of sounds like m n or ng. What are the characteristics categories used to describe consonants.
S voiceless alveolar fricative k voiceless velar plosive n voiced alveolar nasal f voiceless labiodental fricative l voiced alveolar lateral approximant t voiceless alveolar plosive. O p ʍ f θ t s tʃ ʃ k ʔ h have the MoA feature -voice. The passive articulator is the surface on which the constriction is created.
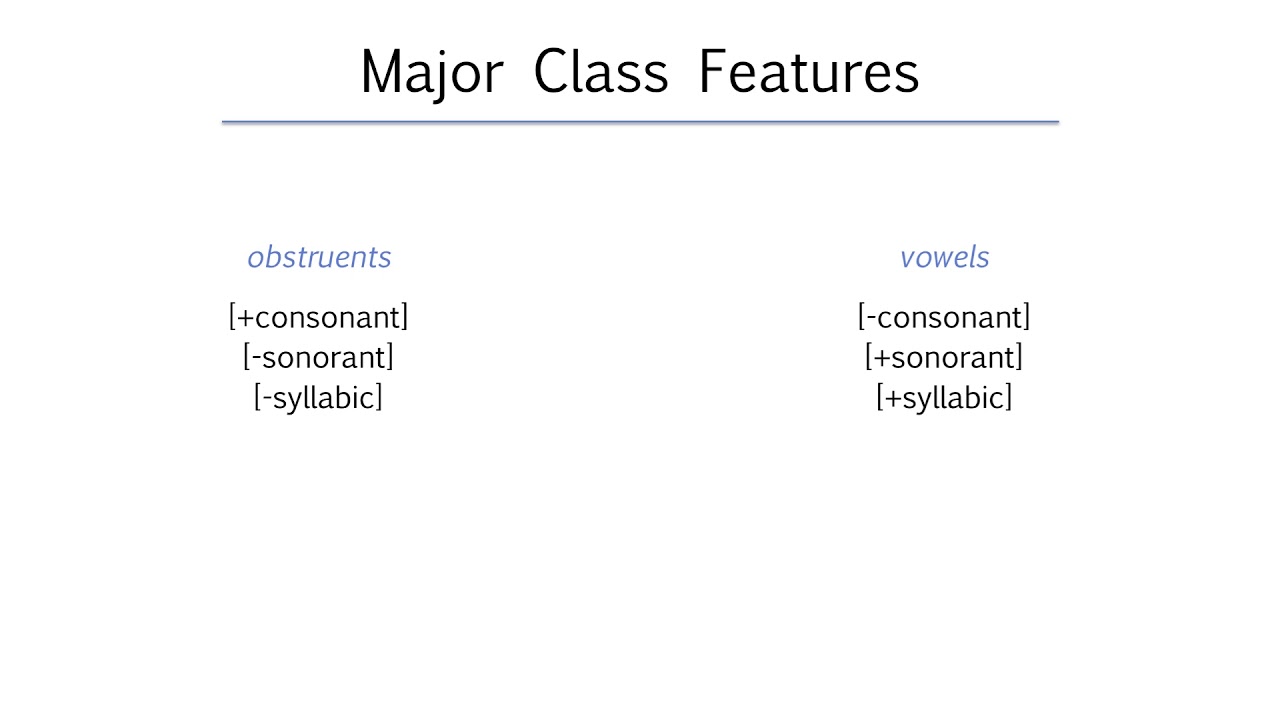
Consonants have two primary classifying characteristics. Vowels and diphthongs are also voiced sounds. Voice onset time and location.
Voiced consonants are produced while the vocal folds are vibrating. Voicing place of articulation and manner of articulation. The word vowel comes from the.
J ɡ ŋ have the MoA feature voice -voiced consonants are produced without the vocal folds vibrating. Consonants in English are pulmonic. Consonants are pronounced in the vocal tract usually in the mouth.
What is voice onset time VOT. In the past the term frictionless continuants was used to describe the characteristics of approximations. A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract.
A w is essentially an u that is acting as a consonant rather a vowel. Word-initially and word-finally these consonants can be devoiced ie they lose part of their voicing. Consonants are sounds produced with the vocal tract restricted or completely closed.

Classification Of Consonants And Vowels Chart Vowel Chart Consonant Speech Language Pathology Grad School

0 Comments